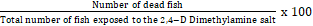Acute Toxicity of Clarias Gariepinus Fingerlings Exposed to 2,4-D Dimethylamine Salt
Abstract
This study investigated the acute toxicity of Clariasgariepinusfingerlings. The fingerlings of Clariasgariepinuswere acclimatized for 1 week before the range-finding test was carried out at varying concentrations. Sublethal concentration (viz: 0.00ppm, 10.80 ppm, 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm of the 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt) were made in a rectangular aquarium. Each experimental concentration was carried out in triplicate with 10 fish each. The media were renewed at every 24 hours throughout the experimental duration viz: 96 hours. When the fish were introduced into the aquarium containing the toxicants, they exhibited some behavioural changes including opercular movement, air gulping and irregular swimming pattern. The mortality rate significantly increased as the concentration of the 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt increased for each of the exposure duration. The LC50 values at 24, 48, 72 and 96 were 86.15 ppm, 36.28 ppm, 18.72 ppm and 15.68 ppm, respectively. From the findings of this study, there is a need for exercise caution in the use of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt based herbicides close to the aquatic ecosystem.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Fuwen Yuan, Duke University, USA
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2020 Enetimi Idah Seiyaboh, et al.
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Pesticides have been found useful in the control of different kind of pest in both homes and agricultural fields 1. Pesticides are often classified based on the target organisms. For instance, the group of pesticides used to control, mitigate or eradicate pests include insecticides, acaricides, herbicides, fungicides, rodenticides, fumigants. According to Inyang et al. 2, pesticides can also be grouped based on the formulation (soluble in solvent or dust-like), origin (synthetic or organic) and mode of action (contact or systemic).
In recent times, the use of herbicides in controlling weeds in agricultural and home fields have increased. This has raised the concern of many environmentalists, possibly due to the toxicity nature of many herbicides to non-targeted organisms. Herbicides just like other pesticides (such as insecticides, acaricides, etc) tend to cause pollution in the environment depending on the concentrations and exposure duration. Over a prolonged period, herbicides could cause an alteration in the biochemical and physiological responses of exposed organisms especially fishes in the aquatic ecosystem and small mammals such as rabbits in the terrestrial environment.
Several herbicides have been studied in different parts of the world. But in Nigeria, some of the commonly used herbicides for controlling weeds in agricultural setting include paraquat dichloride 3, 4, glyphosate 5 and 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt 6. The toxicity of some of these herbicides such as glyphosate and paraquat dichloride have been widely reported in the literature with respect to enzymatic, haematological, histopathological, biochemical, morphological/behavioural responses and mortality rate on fishes.
One of the herbicides that have not been commonly studied and are used for the control of weeds is 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt. Most herbicides that have 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt as the active ingredient is used as a selective, pre-emergent and post-emergent systemic herbicide which diminishes the number of broad leaves weeds and vegetation in agricultural field 6 of both annual and perennial plants.
Most chemical toxicants have the tendency to persist for some time in the environment depending on its nature, concentration and prevailing climatic/ environmental condition. 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt tends to persist in the soil for a long period. According to Inyang et al. 6, 2,4-D Dimethylamine could bioaccumulate in animals (including rabbits, fishes etc) and vegetation which are food source of humans.
Generally, herbicides may find its way into the aquatic ecosystem when they are applied close to surface water resources, and/ or when empty cans of herbicides are discharged into the water bodies directly. Runoff resulting from precipitation are the major methods through which pesticides enter the aquatic ecosystem 3, where they impact on the water quality and some of the associated fauna and flora.
Fish have been widely used to assess the effect of herbicides such as 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt on surface water resources. Toxicants such as herbicides could cause dysfunction in the reproductive, food conversion efficiency, growth, and mortality rates in fishes 3. Hence, this study assessed the mortality rate of Clariasgariepinus fingerlings exposed to 2,4-Dimethylamine salt.
Materials and Methods
Fish Sources and Acclimatization
A total of two hundred and ten Clariasgariepinusfingerlings (mean length of 5.6cm) were procured from a private fish farm in Yenagoa metropolis, Bayelsa state, Nigeria. The fish were acclimatized to an ambient environmental condition in a rectangular aquarium. A sub-lethal concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt was made and renewed daily. During the process, the fish were fed with their normal coupen fish diet (fish meal).
Range Finding Test (Trial Test)
A renewal bioassay was employed in this study, and the solution of the 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt was renewed daily. A range-finding test of the toxicants was carried out at 10ppm, 25ppm, 40ppm and 55ppm. This was done to define a safe sub-lethal concentration for the main experimental run. Each of the concentrations made for the trial test contains 4 fishes.
Main Experiment
About 0.00mls, 0.15mls, 0.25mls, mls, 0.35 mls, 0.45 mls and 0.55 mls of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt (720g/L) (equivalent to 720000 mg/L) was pipetted into rectangular aquarium containing 10 litres of water (equivalent to 10000 mg/L). This brings the concentration to 0.00ppm, 10.80ppm, 18.00ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm. Each of the experimental groups contains 10 fish. Each group was carried out in triplicate. The toxicant was renewed after 24 hours until the experiment was terminated at 96 hours. These concentrations were made by using the formula previously described by Inyang et al. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, Aghoghovwia and Izah 4, 5, Akinsorotan et al. 12:
mls x stock solution (mg/L) = aquarium water (ml) x desired concentration (ppm or mg/l).
Mortality Determination
Water Quality Analysis
The in-situ water quality parameters analyzed include pH, temperature, conductivity, turbidity, dissolved oxygen and salinity and the results obtained ranged from 6.3 – 6.8, 24 - 26 ºC, 61.5 – 136.8 µS/cm, 3.6 – 7.0NTU, 5.2 – 6.5 mg/L and 0.02 – 0.05 ‰, respectively.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical package for social sciences version 20 and graph pad prism 5 was used for the statistical analysis. The data were expressed mean ± standard error, and the charts were plotted using Graph pad prism 5 and Microsoft excel. One way analysis of variance was used to show significant deviations at p=0.05, and Duncan statistics were used to determine the source of observed dissimilarity at p=0.05 The LC50 values were calculated using Finney Table – Microsoft excel regression method as previously applied by Aghoghovwia and Izah 4, 5, Aghoghovwia et al. 3, 15, Izah 16.
Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the percentage mortality of Clariasgariepinus fingerlings exposed to 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt. The percentage mortality at 0.00ppm, 10.80 ppm, 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm was 0.00±0.00 %, 13.33±3.33%, 23.33±3.33%, 26.67±3.33%, 30.00±0.00% and 33.33±3.33%, respectively at 24 hours, being significantly different at p<0.05. Duncan test statistics showed that there is no significant deviation (p>0.05) between 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm and 32.40 ppm concentration of the toxicant. At 48 hours, the percentage mortality at 0.00ppm, 10.80 ppm, 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm was 0.00±0.00 %, 23.33±3.33%, 33.33±3.33%, 40.00±5.77%, 46.67±3.33% and 53.33±3.33%, respectively. There were significant discrepancies at p<0.05 across the various concentration of the toxicant. At 72 hours, the percentage mortality at 0.00ppm, 10.80 ppm, 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm was 0.00±0.00 %, 33.33±8.82%, 53.33±3.33%, 60.00±5.77%, 63.33±6.67% and 66.67±3.33%, respectively. Apart from 0.00 ppm and 10.80 ppm concentration, there was no significant deviation at p>0.05 among the different concentrations. The percentage mortality at 0.00ppm, 10.80 ppm, 18.00 ppm, 25.20 ppm, 32.40 ppm and 39.60 ppm was and 0.00±0.00 %, 36.67±6.67%, 56.67±3.33%, 63.33±8.82%, 73.33±8.82% and 83.33±8.82%, respectively at 96 hours. Statistically, there was dissimilarity (p<0.05) in the percentage mortality. The result showed that as the concentration of the toxicant increased the mortality rate of the fish also increased. This trend have been variously reported when fish are exposed to toxicants including the work of Aghoghovwia and Izah 4, 5 that exposed Heterobranchusbidorsalis fingerlings to paraquat dichloride and glyphosate; Seiyaboh and Izah 17 that exposed Heterobranchusbidorsalis fingerlings to cassava wastewater; Aghoghovwia et al. 3 that exposed Clariasgariepinus to paraquat dichloride; Aghoghovwia et al. 15 that exposed Oreochromis niloticus and Clariasgariepinus to palm oil mill effluents; Akinsorotan et al. 12, Ladipo et al. 18, Ariyo et al. 19 that exposed Oreochromis niloticus, Clariasgariepinus and Labeorohitato paraquat dichloride; Ayoola 20, Nwani et al. 21 that exposed Oreochromis niloticus juvenile and Tilapia zillito glyphosate; Nwani et al. 22 that exposed Channa punctatus to Carbosulfan, Glyphosate and Atrazine; Ojesanmi et al. 23 that exposed Clariasgariepinus fingerlings to 2, 3- dichlorovinyl dimethyl Phosphate; and Oyoroko and Ogamba 13 that exposed Heterobranchusbidorsalis and Clariasgariepinus fingerlings to detergent containing linear alkyl benzene sulphonate. The mortality is often proceeded by behavioural changes which are characterized by moderate swimming and opercular movement, body pigmentation, Intermittent swarming and Jerky movement, increased surfacing and air gulping 3, 13, 14, 15.
Figure 1.Mortality rate of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings exposed to 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt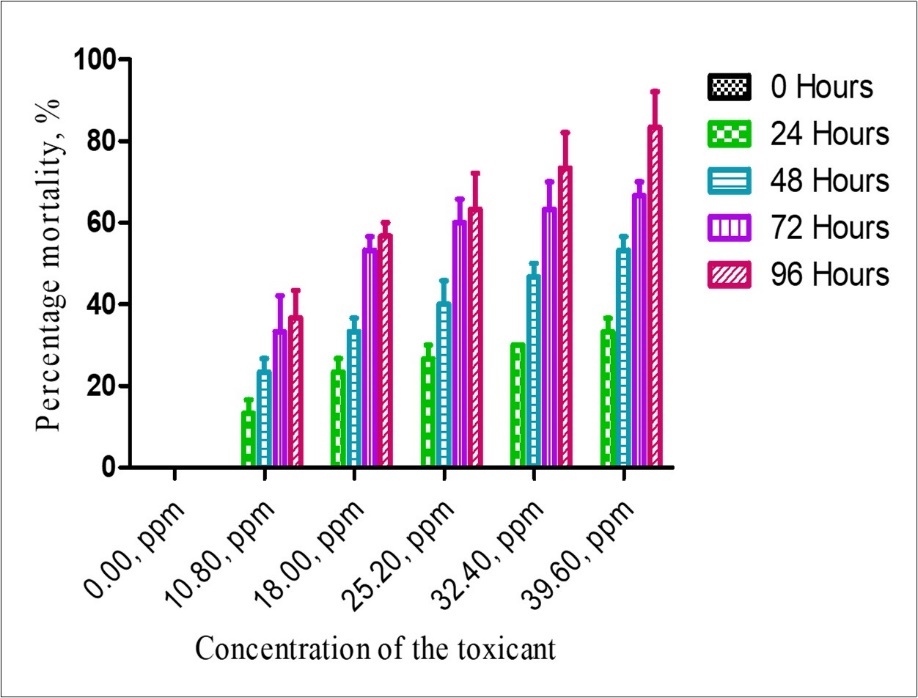
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 shows the LC50 values of Clariasgariepinus fingerlings exposed to 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt. The LC50 values at 24, 48, 72 and 96 were 86.15 ppm, 36.28 ppm, 18.72 ppm and 15.68 ppm, respectively. The LC50 values decreased as the concentration of the toxicant increased. This indicates that as the concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt increased, its toxicity to fish increased. This trend is in line with the findings of authors when different fishes are exposed to different toxicants 3, 4, 5. Though, slight variation exists in the LC50 values. Authors have attributed the variation to fish species, age, size and biochemical makeup of the fishes as well as the type of the toxicants 3, 4, 5. As the acute toxicity duration increases, it could alter the cellular and biochemical processes in fish due to possible changes in enzymatic, haematological, histopathological, physiological and metabolic processes due to hassle and stress.
Figure 2.LC50 of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings exposed to varying concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt after 24 hours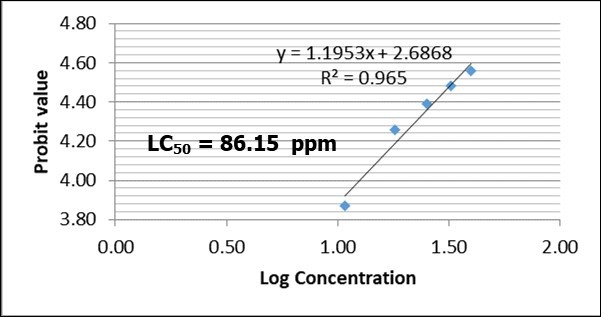
Figure 3.LC50 of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings exposed to varying concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt after 48 hours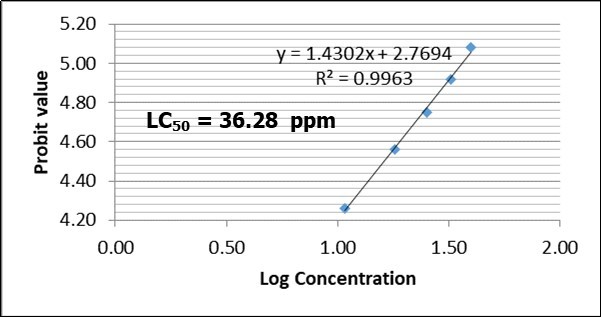
Figure 4.LC50 of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings exposed to varying concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt after 72 hours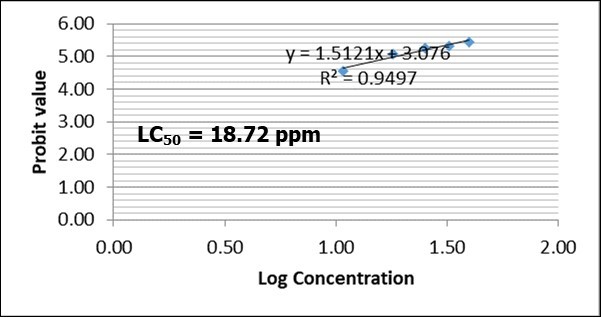
Figure 5.LC50 of Clarias gariepinus fingerlings exposed to varying concentration of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt after 96 hours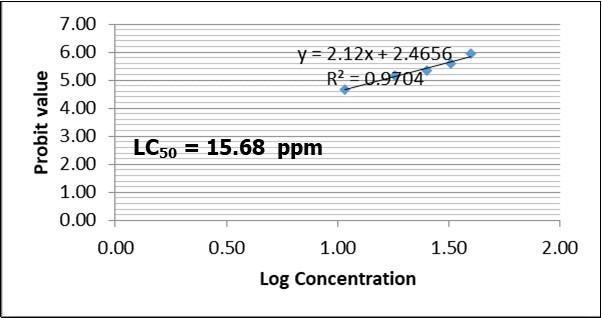
Conclusion
In recent times, the rate of pesticides use especially herbicides have increased. Different brands of herbicides are marketed in Nigeria. This study evaluated the acute toxicity of 2,4-D Dimethylamine to Clariasgariepinusfingerlings. The study found that the mortality rate decreased as the concentration of the toxicant and exposure increased. LC50 values of 15.68 ppm after 96 hours is an indication that the 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt is toxic to fingerlings of Clariasgariepinus. As such, there is the need to exercise caution in the use of 2,4-D Dimethylamine salt based herbicides for the control of grasses especially in the coastal region where surface water resources abound.
References
- 1.Inyang I R, Ollor A O, Izah S C. Common Niger Delta Wetland Fish) (2017) . Effect of Diazinon on Organosomatic Indices and Behavioural Responses ofClariasgariepinus(a , Greener Journal of Biological Sciences 7(2), 15-19.
- 2.Inyang I R, Obidiozo O Z.Izah SC (2016). Effects of Lambda cyhalothrin in protein and Albumin content in the kidney and liver ofParpohiocephalusobscurus.EC Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2(3), 148-153.
- 3.Aghoghovwia O A, Morgan P I, Izah S C. (2019) Behavioral Response and Acute Toxicity of Fingerlings of African Cat Fish,ClariasGariepinusExposed to Paraquat Dichloride. , Journal of Plant and Animal Ecology 1(3), 13-20.
- 4.Aghoghovwia O A.Izah SC (2018). Acute Toxicity of Paraquat Dichloride Based Herbicide againstHeterobranchusbidorsalisFingerlings. , EC Agriculture 4(2), 128-132.
- 5.Aghoghovwia O A.Izah SC (2018). Toxicity of glyphosate based herbicides to fingerlings ofHeterobranchusbidorsalis. , International Journal of Avian & Wildlife Biology 3(5), 397-400.
- 6.Inyang I R, Patani D E, Izah S C. (2020) The Effect of 2,4 Dimethylamine salt on the Blood, Liver and Muscle ofOryclotaguscuniculus. , Journal of Plant and Animal Ecology 1(3), 21-28.
- 7.Inyang I R, N C Okon, Izah S C. (2016) Effect of glyphosate on some enzymes and electrolytes inHeterobranchusbidosalis(a common African catfish). , Biotechnological 2(4), 161-165.
- 8.Inyang I R, Kenobi A.Izah SC (2016). Effect of dimethoate on some selected metabolites in the brain, liver and muscle ofClariaslazera. , Sky Journal of Biochemistry 5(4), 63-68.
- 9.Inyang I R, Thomas S, Izah S C. (2016) Activities of electrolytes in kidney and liver ofClariasgariepinusexposed to fluazifop-p-butyl. , Journal of Biotechnology Research 2(9), 68-72.
- 10.Inyang I R, Thomas S.Izah SC (2016). Evaluation of Activities of Transferases and Phosphatase in Plasma and Organs ofClariasgariepinusExposed to Fluazifop-p-Butyl. , Journal of Environmental Treatment Techniques 4(3), 94-97.
- 11.Inyang I R, Seiyaboh E I, Job U B. (2017) Condition Factor, Organosomatic Indices and behavioural Abnormalities ofClariasgariepinusexposed to Lambda Cyhalothrin. , Greener Journal of Life Sciences,4 1, 001-005.
- 12.Akinsorotan A M, Ajisodun A F, Izah S C, Jimoh J O. (2019) Acute Toxicity of Paraquat Dichloride on Fingerlings of Oreochromis niloticus. , International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences 7(1), 29-36.
- 13.Oyoroko E.Ogamba EN (2017). Toxicity of Detergent Containing Linear Alkyl benzene Sulphonate on Some Commonly Cultured Fish Species in the Niger Delta. , Journal of Environmental Treatment Techniques 5(2), 72-77.
- 14.Oyoroko E.Ogamba EN (2017). Effects of detergent containing linear alkyl benzene sulphonate on behavioural response of Heterobranchus bidorsalis, Clarias gariepinus and Heteroclarias. , Biotechnological Research 3(3), 59-64.
- 15.Aghoghovwia O A, Ugolo M.Izah SC(2019). Acute Toxicity of Graded Palm Oil Mill Effluents on Nile Tilapia (OreochromisniloticusLinnaeus 1758) and African Sharptooth Catfish (ClariasgariepinusBurchell, 1822) Fingerlings. , Int J Environ & Agri Sci 3, 024.
- 16.Izah S C. (2019) Activities of Crude, Acetone and Ethanolic Extracts of Capsicum frutescens var. minima Fruit Against Larvae of Anopheles gambiae. , Journal of Environmental Treatment Techniques 7(2), 196-200.
- 17.Seiyaboh E I.Izah SC (2018). Mortality Rate of JuvenileHeterobranchusbidorsalisExposed to Cassava Mill Effluents. , Annals of Review and Research; 4(1), 555628.
- 18.Ladipo M K, Doherty V F, Oyebadejo S A. (2011) Acute Toxicity, Behavioural Changes and Histopathological Effect of Paraquat Dichloride on Tissues of Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). , International Journal of Biology 3(2), 67-74.
- 19.Arivu I, Muthulingam M, Jiyavudeen M. (2016) Toxicity of paraquat on freshwater fingerlings ofLabeorohita(Hamilton). , International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research 7(10), 1965-1971.
- 20.Ayoola S O. (2008) Toxicity of glyphosate herbicide on Nile tilapia (Oreochromisniloticus) juvenile. , African Journal of Agricultural Research,3 12, 825-834.
- 21.Nwani C D, Ibiam U A, Ibiam O U, Nworie O, Onyishi G et al. (2013) Investigation on acute toxicity and behavioral changes in tilapia zillii due to glyphosate-based herbicide, forceup. , The J. Ani. Plant Sci 23(3), 888-892.
Cited by (2)
This article has been cited by 2 scholarly works according to:
Citing Articles:
Sustainable development and biodiversity (2023) OpenAlex